What is the difference between private and public cloud
There is a lot of talk of the next level virtualization being taken to the “cloud”. There are essentially three kinds of virtualization cloud infrastructure available, they are predominantly private and public clouds and recently a Hybrid cloud, which is a fusion of private and public cloud. In this article we will explain what is the difference between private and public cloud. Although the definitions and roles can vary for a private and public cloud, we will try to give you the best overall perspective for the virtualization cloud. For additional cloud information, check this link right here now!
Difference between private and public cloud depends on the location:
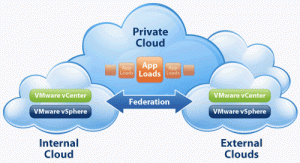
The biggest determining factor between the private and public cloud is the location, in private cloud the services and the infrastructure is located within the boundaries and controls of the organization providing the cloud. By boundaries and controls, I mean that the physical location of the virtualization servers and services is within the corporation, under direct control and within the realms of its on network and firewall controls.
If the service and infrastructure providing the cloud services is located outside the bounds and controls of the enterprise using the services, then it is the public cloud. Mostly, Public cloud services are located and accessed through the internet.
Service and fee models for public and private cloud:
Public cloud services usually based and accessed through the internet charge end users on a per month basis. For example, end users are charged of the public cloud might be charged according to the Bandwidth they use per month, the storage they use or the services provided by licensed services such as SQL server, Windows Servers etc. The great thing about public cloud services is that enterprises don’t need to have the infrastructure needed to host the virtual infrastructure, they simply use what they need and pay according to it.
Private cloud is created with in house services provided by the enterprise. Services are not shared with users outside the enterprise and its customers. Its private and secure, data lives within the enterprises servers etc. For example, virtual desktops provided to users in an enterprise is a private cloud. Administrators in that scenario, can scale deployment of desktops, provide desktops quickly based on templates and creating a desktop with required applications takes minutes instead of days (think about procuring hardware, installing OS, applications etc).
Common Advantages of Private and Public Cloud:
Both Private and Public cloud virtualization has some common advantages that make them very attractive. Some common advantages are:
– Scalability, you can grow the infrastructure on demand
– Charge back provisioning, you can very easily retask and re allocate licensing when you the application needs to be transferred from one user or desktop to another
– Greatly reduces time required to deploy and use new desktop, servers or application
– Central management of hardware, software, applications, users through policies, patch management etc.
What is a Hybrid Cloud:
A Hybrid cloud is a combination of private and public cloud. Users and organizations can “oursource” some of the services to the public cloud, this model works well for non in house applications etc.